Finance Minister of India, Mr. Arun Jaitley said, “There is a need to change the national attitude so that plastic currency becomes the norm and cash an exception”.
Why is there such a big focus of government towards changing people’s payment habits?
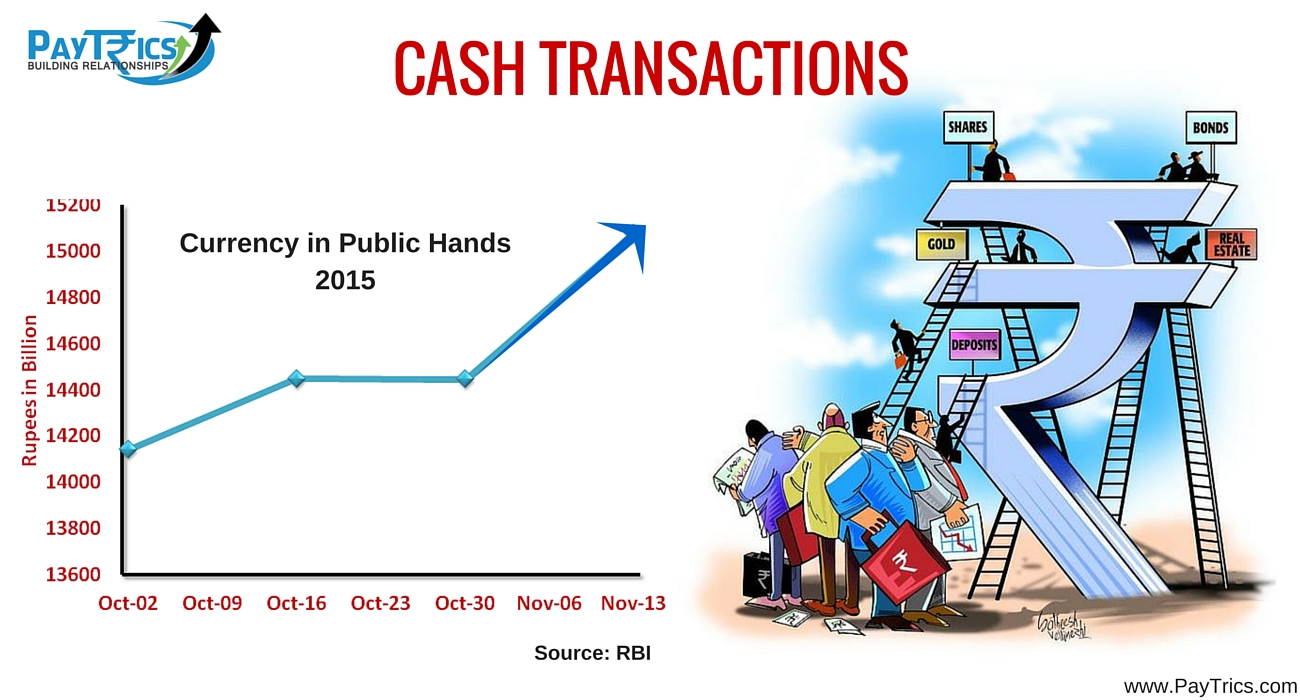
According to RBI data, cash still accounts for 90 per cent of all monetary transactions in India.
As per the report published by “The Hindu” in 2014,
These facts act as an eye opener for a citizen who is surrounded by digital India. But there is a big digital divide in the country which is leading to the above numbers.
Cash Transactions – Why people are transacting in cash?
- Black money: The existence of black money in the country is one of the core reasons why people love transacting in cash. In order to evade income tax or any other tax burden, people start accumulating black money which is nothing but conversion of white money i.e. bank balance in to cash/black money to cleverly play with the tax burden.
- Ease of transaction: In the first decade of twenty first century, the means to transact other than cash were very less and the reach of the digital means were restricted. The most popular modes for retail transactions were cheque and demand draft. There exists a risk of default in case of cheque payments therefore people used to avoid accepting cheques. Demand draft creation was a chargeable service and payer used to try to save that charge.
- Internet Connectivity: Still major part of India is not connected to internet with a speed of even 128kbps which reduces the possibility of internet transactions. 2G Mobile internet does not give good internet connectivity speed and therefore users are unable to transact.
- Fear: Other than fear of tax, Indians are scared of using online means of payment. The small merchants having bank accounts do not opt for internet banking to prevent their account from online theft or any cyber crime. This is the biggest myth in current digital scenario of India. Even people don’t carry their debit cards while shopping as some are scared of losing it.
- Transaction Charges: Some amount of charges are levied by RBI and payment gateway service providers on transactions executed online. These charges range from 0.75%-2.5%. Majority of the retailers/merchants or service providers do not pass on the burden of transaction charges on to the customers. In order to save these charges, people use cash instead of cards.
Government is planning various initiatives to bring down the volume of cash transactions in India. Jan Dhan Yojana is a key initiative to curb that digital divide as well as to increase the reach of banking to every Indian family. Government is also planning to bring some tax and other incentives for people who will boost e-transaction and help government in reducing cash transactions.
In the next article we will talk about the small initiatives which government and citizens of India can take to reduce the volume of cash transactions.














Pingback: Black Money Disclosure: Turmoil Behind 31% or 45%
Pingback: BHIM App Cashback Program for Merchants Launched - Finance Minutes